CSS tutorials for beginners: Learn CSS step-by-step with WebTutor.dev
CSS, or Cascading
Style Sheets, is a stylesheet language used to describe the
presentation of a document written in HTML or XML. CSS allows web developers to
separate the presentation of a web page from its content, making it easier to
maintain and update. CSS works by using selectors to target specific elements
on a web page and applying styles to them. Styles can be applied to individual
elements or to groups of elements, and can include properties such as font
size, color, background color, padding, margin, and more.
CSS provides a powerful and flexible way to style web pages, allowing developers to create beautiful and responsive designs that work across different devices and screen sizes. By mastering CSS, you can take your web development skills to the next level and create stunning websites that stand out from the crowd. To get started with CSS, you will need to learn the basics of CSS, including selectors, properties, and values. You can then start experimenting with different styles and layouts to create unique designs for your web pages. There are many online resources available for learning CSS, including tutorials, videos, and courses, like Google CSS, WebTutor so you can choose the method that works best for you.
3 Methods to Add CSS to Your Web Page
To add CSS
to a web page, you can use one of the following three methods:
Inline CSS: Inline CSS is added directly to the HTML element using
the "style" attribute. For example, to set the text color of a
paragraph to red, you can use the following code:
<p style="color: red;">This text is
red.</p>
Internal CSS: Internal CSS is added to the head
section of the HTML document using the "style" tag. For example:
<head>
<style>
p { color:
red; }
</style>
</head> <body>
<p>This text
is red.</p>
</body>
External CSS: External CSS is added to a separate CSS
file with a ".css" extension. The CSS file is then linked to the HTML
document using the "link" tag in the head section of the HTML
document. For example:
<head>
<link
rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
</head> <body>
<p
class="red">This text is red.</p> </body>
Understanding the Basics of CSS Syntax and CSS Selectors
CSS syntax
consists of a selector followed by one or more declarations enclosed in curly
braces. A declaration consists of a property, followed by a colon, and a value,
separated by a semicolon.
CSS
selectors, on the other hand, are used to target specific elements on a
web page and apply styles to them. Selectors can target elements based on their
element type, class, ID, attribute values, and more.
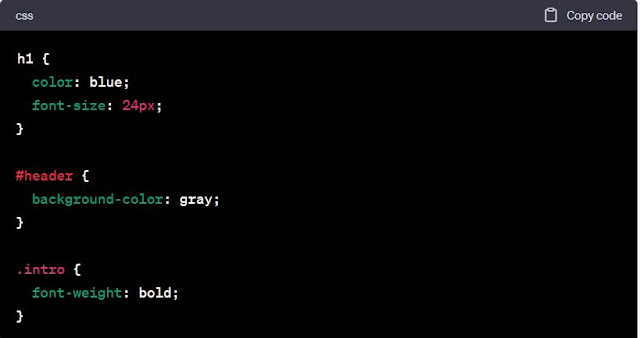
For example, consider the following CSS code:
In this example, h1 is an element type selector that targets
all h1 elements on the web page, #header is an ID selector that targets the
element with the ID of "header," and. intro is a class selector that
targets all elements with the class of "intro."
By mastering
both CSS syntax and selectors, developers can create effective and
efficient stylesheets that apply styles to their web pages in a targeted and
precise manner. There are many online resources available for learning CSS,
including tutorials, and courses, making it easy to get started with CSS and
advance your skills.
By mastering
the syntax of CSS, developers can create effective and efficient
stylesheets that apply styles to their web pages in a targeted and precise
manner.
Additional information about CSS comments
CSS comment syntax used to add notes or reminders to the stylesheet for developers to reference later. They are ignored by the web browser and do not affect the rendering of the web page.
In CSS, comments can be added using two forward slashes (//) or by enclosing the comment in /* and */.
Example
/* This is a CSS comment that spans multiple lines.
You can add any notes or reminders here that can help you or
other developers understand the code. */
h1 {
color: blue; /* This
sets the color of all h1 elements to blue */
}
In this example, the first line is a CSS comment that spans
multiple lines and is enclosed in /* and */. The comment is used to provide
additional information about the code that follows.
The second comment is a single-line comment that starts with
//. It is used to provide information about the line of code that follows it.
By using comments in CSS, developers can make the code more readable, maintainable, and easier to understand.
Overview of CSS colors
Colors are an important aspect of CSS
and are used to style HTML elements with various shades, tints, and hues. In
CSS colors can be defined using keywords, RGB values, HEX values, HSL values,
and more.
Keywords: CSS provides a set of predefined color keywords,
such as red, blue, green, black, and white, among others.
RGB values: RGB stands for Red, Green, Blue and is a
color model used to represent colors in digital devices. RGB values range from
0 to 255 for each color, where 0 represents no intensity and 255 represents
full intensity. RGB values can be defined using the rgb() function, like so:
rgb(255, 0, 0).
HEX values: HEX values are another way to represent
RGB colors in hexadecimal format. HEX values start with a # symbol and are
followed by a combination of six letters and numbers that represent the
intensity of the red, green, and blue components. For example, #FF0000
represents the color red.
HSL values: HSL stands for Hue, Saturation, Lightness
and is another way to define colors in CSS. HSL values can be defined using the
hsl() function, where the hue is represented by a value between 0 and 360
degrees, the saturation and lightness values range from 0% to 100%. For
example, hsl(0, 100%, 50%) represents the color red.
By using any of these color formats, developers
can add a wide range of colors to their web pages and style their HTML elements
in different ways.


Comments
Post a Comment